AI Agent is a trending term in the technology sector in 2025. It can be said that AI Agents serve as a stepping stone before humanity enters the era of super artificial intelligence. So, what exactly is an AI Agent? Why does it have such a significant impact on technological trends? What are some intuitive and easy-to-understand examples of AI Agents? Let’s explore AI Agents from A to Z with Innotech in the article below.
1. What is an AI Agent?
AI Agent – An artificial intelligence agent is an AI system that can observe, reason, and act to perform a specific task. It is like an intelligent assistant that can automatically collect information, analyze data, and make decisions without much human intervention.
Some examples to help you better understand AI Agents:
- Google Assistant or Siri: When you ask, “What’s the weather like today?”, the AI listens (collects data), searches for weather information (analyzes data), and responds to you (performs an action).
- The recommendation system on YouTube: When you watch a video, YouTube analyzes your preferences to suggest the next videos you might like.
What are AI Agents
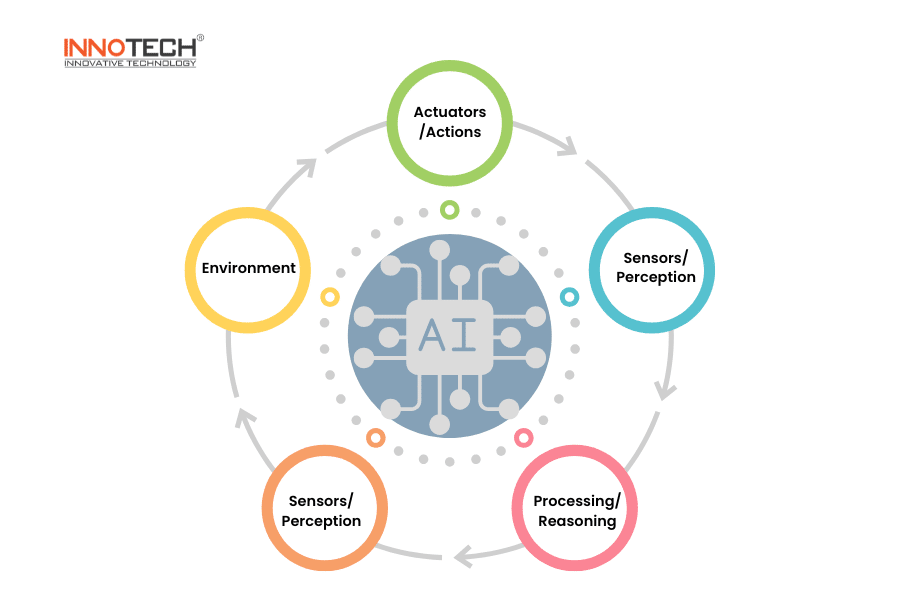
2. The components of an AI Agent.
AI Agents usually have five main components as follows:
- Environment: The world or context in which the AI agent operates, which can be the real world (robots, self-driving cars) or a virtual world (games, software systems).
- Sensors/Perception: Collects data from the environment (camera, microphone, data APIs, etc.).
- Processing/Reasoning: Analyzes data and makes decisions, possibly using machine learning or search algorithms.
- Actuators/Actions: Performs actions based on the decisions made (controlling robots, responding to messages, recommending content).
- Goal/Objective: Defines the task the AI needs to accomplish, such as optimizing search results, navigating a self-driving car, or predicting customer demand.
Components of an AI Agent
2.1. Environment and Interaction of AI Agents
Environment and Interaction of an AI Agent
AI Agents operate in a specific environment, which can be the real world (e.g., self-driving cars, industrial robots) or a virtual world (e.g., chatbots, recommendation systems on YouTube).
Depending on the type of AI Agent, the level of interaction with the environment may vary:
- Passive AI Agent: Only observes and responds based on predefined rules (e.g., automated chatbot).
- Active AI Agent: Analyzes data, learns from the environment, and adjusts its behavior accordingly (e.g., a self-driving car recognizing traffic signals and adjusting speed).
Examples of AI Agent interaction with the environment:
- Self-driving car: Observes lanes, traffic signs, and pedestrians → analyzes the situation → decides to stop, turn, or accelerate.
- Virtual assistant (Siri, Google Assistant): Listens to user commands → analyzes the question → responds with an appropriate answer.
2.2. Sensors – Collecting Information
Sensors help AI Agents observe their surroundings and collect necessary data. The data can come from various sources, such as:
- Images & Video: Cameras on self-driving cars, facial recognition systems.
- Audio: Microphones on virtual assistants (Siri, Google Assistant).
- Digital Data: Browsing history, user behavior on platforms like YouTube and Netflix.
Sensors AI
2.3. Processing Unit – Analysis and Reasoning
After collecting data, the AI Agent requires a processing unit to analyze information and make decisions. This is where artificial intelligence algorithms such as Machine Learning and Deep Learning are applied.
Examples of how the processing unit works:
- A self-driving car detects a red traffic light → analyzes the situation → decides to stop.
- YouTube analyzes your video watch history → recommends relevant content.
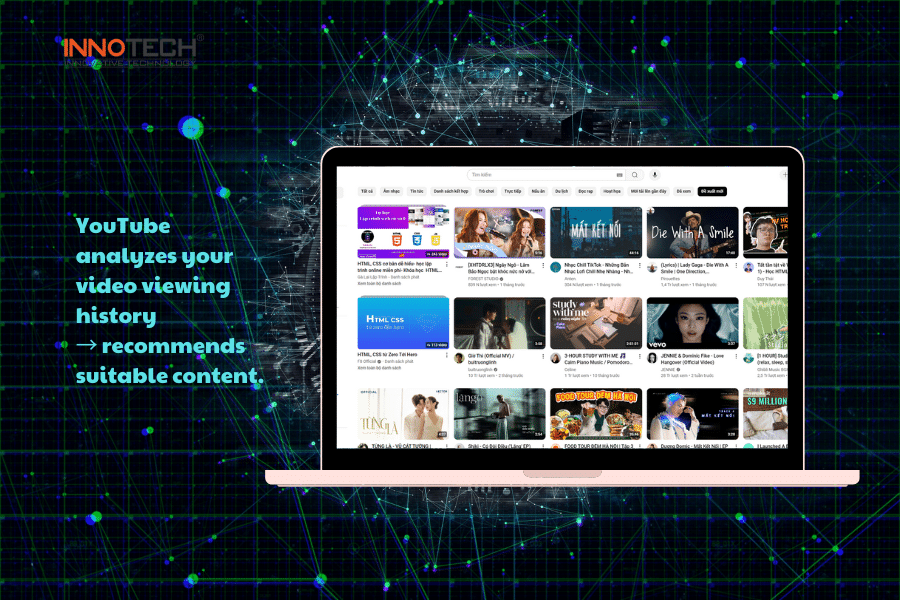
YouTube analyzes your video watch history and recommends relevant content
2.4. Actuators – Taking Action Based on Decisions
After processing the data, the AI Agent performs a specific action to impact the environment.
Examples:
- A self-driving car decides to stop → sends a signal to the braking system to halt the vehicle.
- A chatbot decides on a response → displays the text to the user.
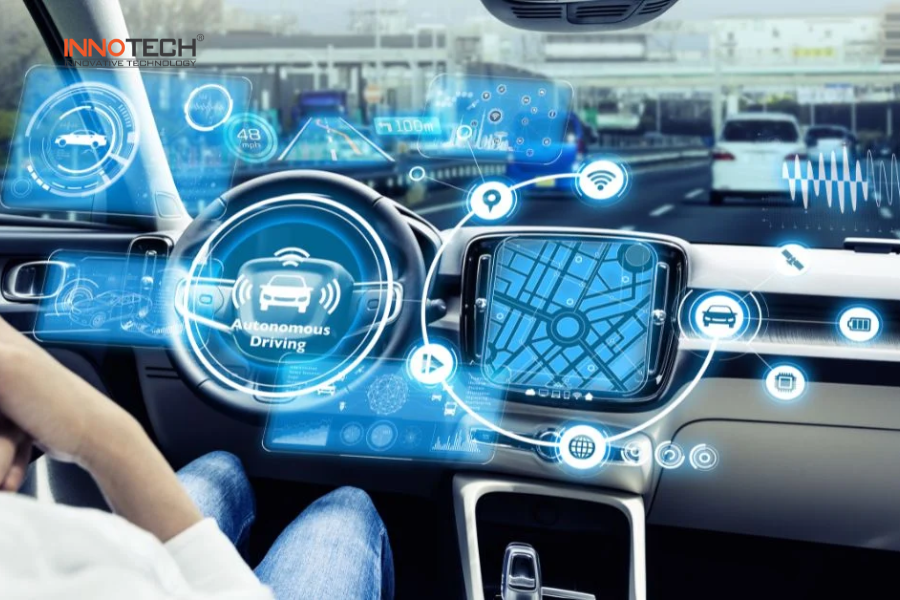

The car automatically decides to stop
2.5. Goals – Guiding the Actions of an AI Agent
Each AI Agent has a specific goal, such as:
- Chatbot: Accurately answering user questions.
- Self-driving car: Traveling safely and arriving at the destination on time.
- AI in finance: Predicting market trends to provide investment advice.
3. Information Processing and Decision-Making Process of an AI Agent
Information processing and decision AI Agent
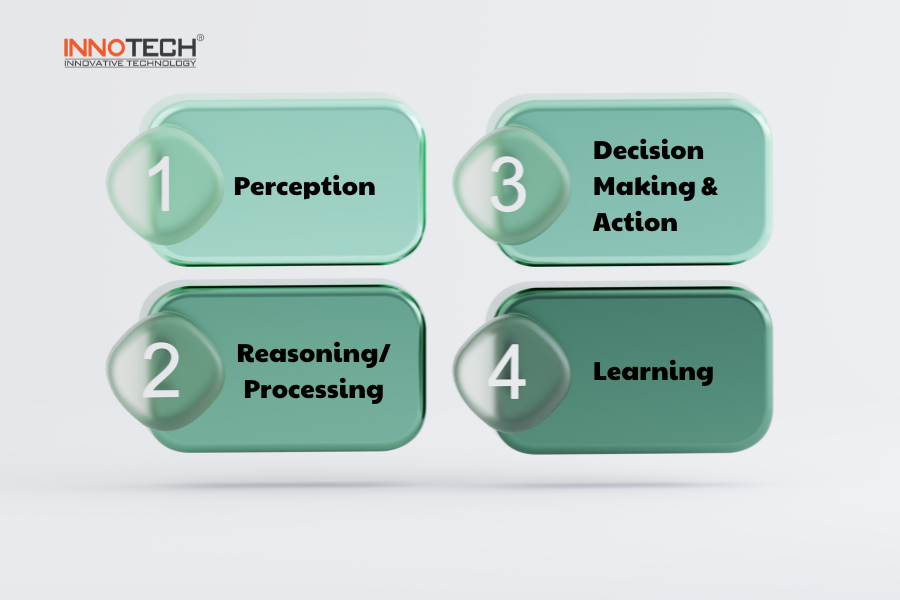
An AI Agent operates through a cycle consisting of four main steps:
Step 1: Collecting Data from the Environment (Perception)
- The AI Agent uses sensors to observe the environment and gather necessary data.
- Example: A self-driving car uses cameras to recognize traffic signs.
Step 2: Analyzing and Processing Information (Reasoning/Processing)
- The processing unit analyzes the data and determines the appropriate action using AI algorithms.
- Example: A self-driving car detects a red light and decides to apply the brakes.
Step 3: Decision Making & Action
- The AI Agent selects the optimal action and uses actuators to execute it.
- Example: A self-driving car sends a signal to apply the brakes.
Step 4: Learning and Improving Performance (Learning – if applicable)
- Some AI Agents can learn from data to enhance their performance over time (Learning Agent).
- Example: Virtual assistants like Google Assistant can learn from previous questions to improve their responses.
4. Classification of AI Agents: Common Types of AI Agents
AI Agents come in various types depending on how they process information and make decisions. Below are five common types of AI Agents, ranging from simple to complex.
4.1. Simple Reflex Agent – Basic Reflex Agent
Definition
- A Simple Reflex Agent makes decisions based on fixed rules, responding directly to the current state of the environment without considering history or predicting the future.
How It Works
- Observes the environment → Checks conditions → Executes actions based on predefined rules.
- No memory, does not learn from experience.
Real-World Examples
- Automatic air conditioner: When the sensor detects a temperature above 30°C, the system turns on the air conditioner.
- Basic collision avoidance system in robots: If an obstacle is detected → Stops or changes direction.
Advantages
- Fast, simple, easy to implement.
Disadvantages
- Lacks flexibility, cannot adapt to new situations.
4.2. Model-Based Reflex Agent – Model-Based Reflex Agent
Definition
- This agent uses a model of the environment to understand and predict the state of the world, allowing it to make more accurate decisions.
How It Works
- Observes the environment → Stores state in memory → Uses the model to reason → Takes action.
- Can consider previous history to provide better responses.
Real-World Examples
- Self-driving car: If it detects a red light, the car not only stops but also predicts when the light will turn green to decide the optimal time to accelerate.
- Smart vacuum cleaner: Remembers the room layout to avoid colliding with fixed obstacles.
Advantages
- More flexible, capable of handling complex situations.
Disadvantages
- Requires memory and higher computational power.
4.3. Goal-Based Agent – Goal-Oriented Agent
Definition
- This agent does not just react based on rules but sets specific goals and then selects the best actions to achieve them.
How It Works
- Observes the environment → Identifies a goal → Plans and selects the best action to achieve the goal.
- Can evaluate multiple options before making a decision.
Real-World Examples
- GPS navigation system: Determines the shortest route from point A to point B based on traffic conditions.
- Virtual assistants (Google Assistant, Siri): When given the command “Schedule a meeting at 10 AM tomorrow,” it checks the calendar and schedules the meeting accordingly.
Advantages
- Flexible and capable of solving problems based on specific goals.
Disadvantages
- Requires more data and complex algorithms.
4.4. Utility-Based Agent – Optimization-Oriented Agent
Definition
- This agent not only sets goals but also finds the best solution to optimize results. It evaluates the utility (usefulness) of each action before making a decision.
How It Works
- Observes the environment → Identifies a goal → Evaluates the utility of each option → Chooses the most beneficial option.
- Considers multiple factors such as cost, time, and risk level.
Real-World Examples
- Tesla self-driving car: Not only selects the shortest route but also considers speed, battery consumption, and traffic conditions to make the optimal choice.
- Recommendation systems on Netflix and YouTube: Suggests content based on personal preferences to maximize user satisfaction.
Advantages
- Makes smarter and more optimized decisions.
Disadvantages
- Requires large amounts of data and complex algorithms.
4.5. Learning Agent – Self-Learning Agent
Definition
- This is the most advanced type of AI Agent, capable of learning and improving over time based on real-world experiences.
How It Works
- Observes the environment → Takes action → Receives feedback → Adjusts behavior to improve future performance.
- Uses Machine Learning to learn from data.
Real-World Examples
- Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo: Learned to play Go and defeated professional players by improving through each match.
- Fraud detection systems in banking: Learns from past transactions to identify suspicious activities.
Advantages
- Becomes smarter and more efficient over time.
Disadvantages
- Requires large amounts of data and powerful computing resources.
Depending on real-world applications, each type of AI Agent has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Simple Reflex Agent is suitable for basic automated systems.
- Model-Based Reflex Agent can handle more complex environments.
- Goal-Based Agent helps with planning and achieving desired outcomes.
- Utility-Based Agent finds the best solution to optimize performance.
- Learning Agent becomes increasingly intelligent by learning from data.
AI Agents are becoming more important and widespread in daily life, from self-driving cars and virtual assistants to intelligent financial systems. In the future, with advancements in artificial intelligence, AI Agents will become even more flexible and intelligent, helping humans solve complex problems more efficiently.
5. Benefits and Challenges of AI Agents
AI Agents are becoming an essential part of many industries due to their ability to automate and optimize workflows. However, alongside their significant advantages, AI Agents also pose various challenges that need to be addressed.
5.1. Benefits of AI Agents
- Automation of Workflows: AI Agents help automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual workloads and increasing efficiency. For example, AI chatbots can answer thousands of customer inquiries simultaneously without human intervention.
- Increased Efficiency and Accuracy: AI Agents can process vast amounts of data faster and more accurately than humans. In healthcare, AI assists in diagnosing diseases through medical imaging, sometimes with higher accuracy than doctors.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Businesses can save costs on hiring personnel for repetitive or high-precision tasks. For example, AI in finance can analyze data and detect fraud without requiring a large monitoring team.
- Improved User Experience: AI Agents personalize customer experiences. For instance, recommendation systems on Netflix and YouTube suggest content based on user preferences, making content discovery more relevant.

Benefits of AI Agent
5.2. Challenges of AI Agents
- Reliability and Accuracy: While AI Agents can make quick decisions, they are not always accurate. Errors in AI systems can have severe consequences, such as self-driving cars misidentifying objects on the road.
- Ethical and Accountability Issues: AI raises ethical concerns, such as potential bias in hiring processes if trained on unfair datasets.
- Security and Privacy Risks: AI Agents collect and process large amounts of personal data. Without proper security measures, user information may be stolen or misused.
- Job Displacement: AI-driven automation may replace traditional jobs, raising concerns about unemployment, especially in manufacturing, customer service, and basic data analysis sectors.
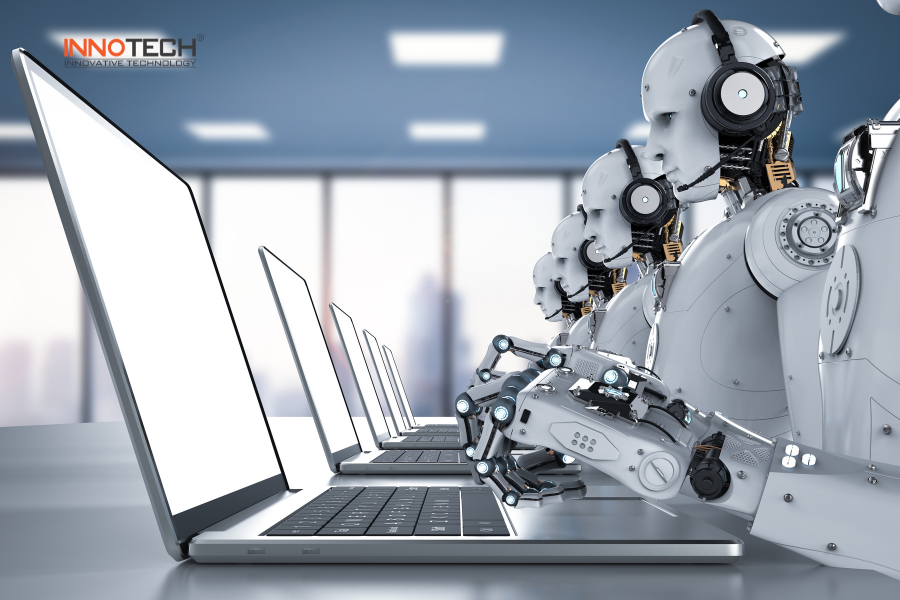

Risk of losing jobs because of AI
6. The Future of AI Agents
In the next 5–10 years, AI Agents will become increasingly intelligent, adaptable, and widely applied across various industries.
6.1. Trends in AI Agent Development
- AI Agents will learn and adapt better: AI will not only follow fixed rules but will also have the ability to learn from experience to improve its decision-making. Algorithms such as Reinforcement Learning will help AI Agents function more like humans.
- More natural interactions: Chatbots and virtual assistants will become more human-like in communication, thanks to advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology.
- Expansion into multiple industries: AI Agents will not be limited to customer service, finance, or healthcare but will also be applied in education, law, and even content creation.
6.2. The Integration of AI Agents with Emerging Technologies
- AI Agents + IoT (Internet of Things): The combination of AI and IoT will allow smart devices to automatically respond to environmental data. For example, smart homes can adjust temperature settings based on user habits.
- AI Agents + Blockchain: Blockchain technology can enhance data security for AI Agents, particularly in fields like finance and supply chain management.
- AI Agents + Metaverse: In the Metaverse, AI Agents can act as virtual assistants or NPCs (non-playable characters), enhancing interactive experiences.
AI Agents have been transforming the way humans work and interact with technology. They enable automation, optimization, and personalization across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and commerce. With their ability to learn, AI Agents are becoming increasingly intelligent, assisting humans in handling complex tasks. AI helps save time, improve work efficiency, and create new opportunities. However, despite these significant benefits, AI also presents challenges related to ethics, security, and the risk of replacing traditional jobs.
The year 2025 is seen as a turning point for AI Agents, making them more widespread and paving the way for artificial superintelligence. This period will witness businesses focusing on digital transformation and AI integration to optimize operations. However, not all companies have expertise in AI Agents or an in-house team for AI model development. Innotech provides custom AI model development services, integrating AI into business systems, and offering AI outsourcing solutions tailored to specific needs.
To receive consultation on AI integration systems, please leave your information here.


